Reputation: 1193
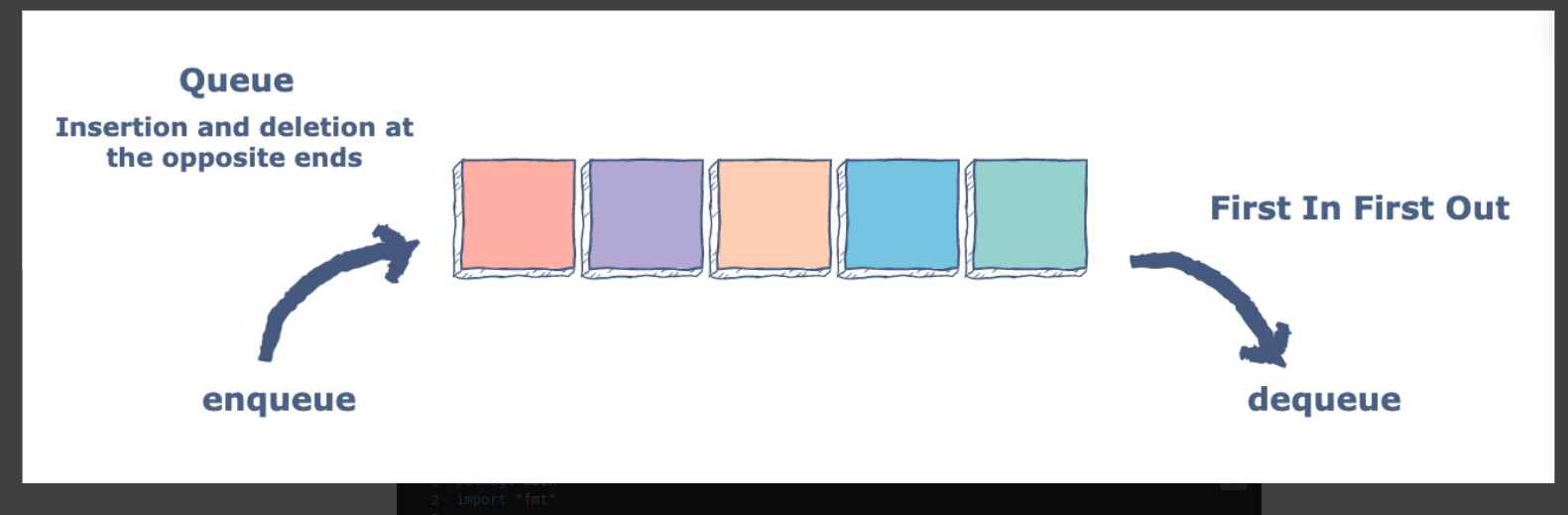
Is there a queue implementation?
Can anyone suggest Go container for simple and fast FIFO/queue, Go has 3 different containers: heap, list and vector. Which one is more suitable to implement a queue?
Upvotes: 119
Views: 170004
Answers (20)
Reputation: 87
You can implement a queue in Go using the container/list package.
The container/list package provides a doubly linked list implementation, which is well-suited for queue operations because it allows efficient insertion and removal from both ends of the list. This can be more efficient than using slices for large datasets.
Here’s an example of using container/list to implement a basic queue:
package main
import (
"container/list"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
queue := list.New()
queue.PushBack(1)
queue.PushBack(2)
queue.PushBack(3)
fmt.Printf("Queue size %d\n", queue.Len())
n := queue.Remove(queue.Front())
fmt.Printf("Popped: %d, Queue size: %d\n", n, queue.Len())
n = queue.Remove(queue.Front())
fmt.Printf("Popped: %d, Queue size: %d\n", n, queue.Len())
n = queue.Remove(queue.Front())
fmt.Printf("Popped: %d, Queue size: %d\n", n, queue.Len())
}
Result:
Queue size 3
Popped: 1, Queue size: 2
Popped: 2, Queue size: 1
Popped: 3, Queue size: 0
Upvotes: 1
Reputation: 9
package queue
type Queue struct {
data []any
}
func (q *Queue) Enqueue(d any) {
q.data = append(q.data, d)
}
func (q *Queue) Dequeue() any {
dequeued := q.data[0]
q.data = q.data[1:]
return dequeued
}
func (q *Queue) IsEmpty() bool {
return len(q.data) == 0
}
func NewQueue() *Queue {
return &Queue{
data: make([]any, 0),
}
}
Upvotes: -1

Reputation: 346
The simplest way to implement the queue data structure in Golang is to use a slice.
Since a queue follows a FIFO (First-In-First-Out) structure, the dequeue and enqueue operations can be performed as follows:
- Use the built-in append function to enqueue.
- Slice off the first element to dequeue.
The following code snippet implements a basic queue using a slice. Note how enqueuing and dequeuing occur at opposite ends of the slice.
package main
import "fmt"
func enqueue(queue[] int, element int) []int {
queue = append(queue, element); // Simply append to enqueue.
fmt.Println("Enqueued:", element);
return queue
}
func dequeue(queue[] int) ([]int) {
element := queue[0]; // The first element is the one to be dequeued.
fmt.Println("Dequeued:", element)
return queue[1:]; // Slice off the element once it is dequeued.
}
func main() {
var queue[] int; // Make a queue of ints.
queue = enqueue(queue, 10);
queue = enqueue(queue, 20);
queue = enqueue(queue, 30);
fmt.Println("Queue:", queue);
queue = dequeue(queue);
fmt.Println("Queue:", queue);
queue = enqueue(queue, 40);
fmt.Println("Queue:", queue);
}
Warning(memory-leaks): In the dequeue function above, the memory allocated for the first element in the array is never returned.
We can use dynamic data structure(linked list) in order to avoid memory leaks. The sample code is given below:
package main
import "container/list"
import "fmt"
func main() {
// new linked list
queue := list.New()
// Simply append to enqueue.
queue.PushBack(10)
queue.PushBack(20)
queue.PushBack(30)
// Dequeue
front:=queue.Front()
fmt.Println(front.Value)
// This will remove the allocated memory and avoid memory leaks
queue.Remove(front)
}
Upvotes: 0

Reputation: 83
you can try something like this,
// queue.go
package queue
type Queue struct {
data []int
}
func (q *Queue) Enqueue(d int) {
q.data = append(q.data, d)
}
func (q *Queue) Dequeue() int {
dequeued := q.data[0]
q.data = q.data[1:]
return dequeued
}
func (q *Queue) IsEmpty() bool {
return len(q.data) == 0
}
func NewQueue() *Queue {
return &Queue{
data: make([]int, 0),
}
}
//queue_test.go
package queue
import (
"testing"
"github.com/stretchr/testify/assert"
)
func TestQueue_ShouldInitialiseWithEmpty(t *testing.T) {
q := NewQueue()
assert.Equal(t, true, q.IsEmpty())
}
func TestQueue_ShouldErrorIfDequeuePerformedOnEmpty(t *testing.T) {
q := NewQueue()
_, err := q.Dequeue()
assert.NotNil(t, err)
assert.Equal(t, "nothing to dequeue", err.Error())
}
func TestQueue(t *testing.T) {
q := NewQueue()
q.Enqueue(1)
q.Enqueue(2)
q.Enqueue(3)
q.Enqueue(4)
dequeued1, err1 := q.Dequeue()
assert.Nil(t, err1)
assert.Equal(t, 1, dequeued1)
dequeued2, err2 := q.Dequeue()
assert.Nil(t, err2)
assert.Equal(t, 2, dequeued2)
dequeued3, err3 := q.Dequeue()
assert.Nil(t, err3)
assert.Equal(t, 3, dequeued3)
dequeued4, err4 := q.Dequeue()
assert.Nil(t, err4)
assert.Equal(t, 4, dequeued4)
}
Upvotes: 4
Reputation: 485
From Go v1.18 generics have been added which I would use to make a generic queue.
Below are my implementations
type queue[T any] struct {
bucket []T
}
func newQueue[T any]() *queue[T] {
return &queue[T]{
bucket: []T{},
}
}
func (q *queue[T]) append(input T) {
q.bucket = append(q.bucket, input)
}
func (q *queue[T]) tryDequeue() (T, bool) {
if len(q.bucket) == 0 {
var dummy T
return dummy, false
}
value := q.bucket[0]
var zero T
q.bucket[0] = zero // Avoid memory leak
q.bucket = q.bucket[1:]
return value, true
}
Whenever dequeue is called the queue is resized to release memory using slicing to avoid copying memory. This isn't thread safe, in those cases channels are probably better - but one needs to know the queues capacity to specify a correct buffer size.
For fun I have made a benchmark run against a queue which uses interface{} - the way to have a generic solution before Go v1.18.
The test appends and the dequeues 1, 10, 100 and 1.000 integers. In all cases generics are a lot faster with less memory usages.
Benchmark_queues/QueueGeneric-Size_1-8 38296201 32.78 ns/op 8 B/op 1 allocs/op
Benchmark_queues/QueueInterface-Size_1-8 11626666 147.6 ns/op 16 B/op 1 allocs/op
Benchmark_queues/QueueGeneric-Size_10-8 7846665 168.2 ns/op 160 B/op 2 allocs/op
Benchmark_queues/QueueInterface-Size_10-8 1501284 752.8 ns/op 320 B/op 2 allocs/op
Benchmark_queues/QueueGeneric-Size_100-8 1000000 1088 ns/op 1536 B/op 1 allocs/op
Benchmark_queues/QueueInterface-Size_100-8 240232 6798 ns/op 3072 B/op 1 allocs/op
Benchmark_queues/QueueGeneric-Size_1000-8 120244 13468 ns/op 17920 B/op 3 allocs/op
Benchmark_queues/QueueInterface-Size_1000-8 20310 54528 ns/op 35776 B/op 4 allocs/op
The implementation of queue using interface{} are given below - error handling is added which I think is necessary.
type queueInterface struct {
bucket []interface{}
}
func newQueueInterface() *queueInterface {
return &queueInterface{
bucket: []interface{}{},
}
}
func (q *queueInterface) append(input interface{}) error {
if len(q.bucket) != 0 && reflect.TypeOf(q.bucket[0]) != reflect.TypeOf(input) {
return errors.New("input type not same as those already in queue")
}
q.bucket = append(q.bucket, input)
return nil
}
func (q *queueInterface) tryDequeue(out interface{}) (bool, error) {
if len(q.bucket) == 0 {
return false, nil
}
valuePtr := reflect.ValueOf(out)
if valuePtr.Kind() != reflect.Ptr {
return false, errors.New("must be a pointer")
}
value := q.bucket[0]
if valuePtr.Elem().Type() != reflect.TypeOf(value) {
return false, errors.New("output must be of same type as queue elements")
}
valuePtr.Elem().Set(reflect.ValueOf(value))
var zero interface{}
q.bucket[0] = zero // Avoid memory leak
q.bucket = q.bucket[1:]
return true, nil
}
Upvotes: 4

Reputation: 953
Most queue implementations are in one of three flavors: slice-based, linked list-based, and circular-buffer (ring-buffer) based.
- Slice-based queues tend to waste memory because they do not reuse the memory previously occupied by removed items. Also, slice based queues tend to only be single-ended.
- Linked list queues can be better about memory reuse, but are generally a little slower and use more memory overall because of the overhead of maintaining links. They can offer the ability to add and remove items from the middle of the queue without moving memory around, but if you are doing much of that a list is the wrong data structure.
- Ring-buffer queues offer all the efficiency of slices, with the advantage of not wasting memory. Fewer allocations means better performance. They are just as efficient adding and removing items from either end so you naturally get a double-ended queue. So, as a general recommendation I would recommend a ring-buffer based queue implementation. This is what is discussed in the rest of this post.
The ring-buffer based queue reuses memory by wrapping its storage around: As the queue grows beyond one end of the underlying slice, it adds additional nodes to the other end of the slice. See deque diagram
Also, a bit of code to illustrate:
// PushBack appends an element to the back of the queue. Implements FIFO when
// elements are removed with PopFront(), and LIFO when elements are removed
// with PopBack().
func (q *Deque) PushBack(elem interface{}) {
q.growIfFull()
q.buf[q.tail] = elem
// Calculate new tail position.
q.tail = q.next(q.tail)
q.count++
}
// next returns the next buffer position wrapping around buffer.
func (q *Deque) next(i int) int {
return (i + 1) & (len(q.buf) - 1) // bitwise modulus
}
This particular implementation always uses a buffer size that is a power of 2, and can therefore compute the bitwise modulus to be a little more efficient.
This means the slice needs to grow only when all its capacity is used up. With a resizing strategy that avoids growing and shrinking storage on the same boundary, this makes it very memory efficient.
Here is code that resizes the underlying slice buffer:
// resize resizes the deque to fit exactly twice its current contents. This is
// used to grow the queue when it is full, and also to shrink it when it is
// only a quarter full.
func (q *Deque) resize() {
newBuf := make([]interface{}, q.count<<1)
if q.tail > q.head {
copy(newBuf, q.buf[q.head:q.tail])
} else {
n := copy(newBuf, q.buf[q.head:])
copy(newBuf[n:], q.buf[:q.tail])
}
q.head = 0
q.tail = q.count
q.buf = newBuf
}
Another thing to consider is if you want concurrency safety built into the implementation. You may want to avoid this so that you can do whatever works best for your concurrency strategy, and you certainly do not want it if your do not need it; same reason as not wanting a slice that has some built-in serialization.
There are a number of ring-buffer based queue implementations for Go if you do a search on godoc for deque. Choose one that best suits your tastes.
Upvotes: 31
Reputation: 59
O(1) Time for EnQueue, DeQueue, Front & Rear Lookups O(n) Space for Capacity
type Queue struct {
front int
rear int
size int
capacity int
q []string
}
func (q *Queue) IsFull() bool {
return q.size == q.capacity
}
func (q *Queue) IsEmpty() bool {
return q.size == 0
}
func (q *Queue) EnQueue(s string) error {
if q.IsFull() {
return fmt.Errorf("queue is full")
}
q.rear = (q.rear + 1) % q.capacity
q.q[q.rear] = s
q.size++
return nil
}
func (q *Queue) DeQueue() (string, error) {
if q.IsEmpty() {
return "", fmt.Errorf("queue is empty")
}
defer func() { q.front, q.size = (q.front+1)%q.capacity, q.size-1 }()
return q.q[q.front], nil
}
func (q *Queue) Front() (string, error) {
if q.IsEmpty() {
return "", fmt.Errorf("queue is empty")
}
return q.q[q.front], nil
}
func (q *Queue) Rear() (string, error) {
if q.IsEmpty() {
return "", fmt.Errorf("queue is empty")
}
return q.q[q.rear], nil
}
func (q *Queue) Print() []string {
return q.q[q.front : q.rear+1]
}
func New(capacity int) *Queue {
q := &Queue{
capacity: capacity,
rear: capacity - 1,
q: make([]string, capacity),
}
return q
}
func main() {
queue := New(6)
queue.EnQueue("10")
queue.EnQueue("20")
queue.EnQueue("30")
queue.EnQueue("40")
queue.EnQueue("50")
queue.EnQueue("60")
fmt.Println(queue.EnQueue("70")) // Test Capcacity Exceeded EnQueue.
fmt.Println(queue.Print())
fmt.Println(queue.DeQueue())
fmt.Println(queue.DeQueue())
fmt.Println(queue.DeQueue())
fmt.Println(queue.Print())
fmt.Println(queue.DeQueue())
fmt.Println(queue.DeQueue())
fmt.Println(queue.DeQueue())
fmt.Println(queue.DeQueue()) // Test Empty DeQueue.
fmt.Println(queue.Print())
queue.EnQueue("80")
fmt.Println(queue.Print())
fmt.Println(queue.DeQueue())
fmt.Println(queue.Print())
}
Upvotes: 2

Reputation: 2235
Edit, cleaner implementation of a Queue:
package main
import "fmt"
type Queue []interface{}
func (self *Queue) Push(x interface{}) {
*self = append(*self, x)
}
func (self *Queue) Pop() interface{} {
h := *self
var el interface{}
l := len(h)
el, *self = h[0], h[1:l]
// Or use this instead for a Stack
// el, *self = h[l-1], h[0:l-1]
return el
}
func NewQueue() *Queue {
return &Queue{}
}
func main() {
q := NewQueue()
q.Push(1)
q.Push(2)
q.Push(3)
q.Push("L")
fmt.Println(q.Pop())
fmt.Println(q.Pop())
fmt.Println(q.Pop())
fmt.Println(q.Pop())
}
Or just embed a "container/list" inside a simple implementation and expose the interface:
package queue
import "container/list"
// Queue is a queue
type Queue interface {
Front() *list.Element
Len() int
Add(interface{})
Remove()
}
type queueImpl struct {
*list.List
}
func (q *queueImpl) Add(v interface{}) {
q.PushBack(v)
}
func (q *queueImpl) Remove() {
e := q.Front()
q.List.Remove(e)
}
// New is a new instance of a Queue
func New() Queue {
return &queueImpl{list.New()}
}
Upvotes: 16
Reputation: 51
type Queue struct {
slice []int
len int
}
func newq() Queue {
q := Queue{}
q.slice = make([]int, 0)
q.len = 0
return q
}
func (q *Queue) Add(v int) {
q.slice = append(q.slice, v)
q.len++
}
func (q *Queue) PopLeft() int {
a := q.slice[0]
q.slice = q.slice[1:]
q.len--
return a
}
func (q *Queue) Pop() int {
a := q.slice[q.len-1]
q.slice = q.slice[:q.len-1]
q.len--
return a
}
For your basic need the code above would do
Upvotes: 2

Reputation: 21
list is enough for queue and stack, what we shoud do is l.Remove(l.Front()) for queue Poll, l.Remove(l.Back())for stack Poll,PushBack for the Add Operation for stack and queue. there are front and back pointer for list, such that time complexity is O(1)
Upvotes: 1

Reputation: 10527
Double stack implementation:
O(1) Enqueue and Dequeue and uses slices (which tends to be better for cache misses).
type Queue struct{
enqueue, dequeue Stack
}
func (q *Queue) Enqueue(n *Thing){
q.enqueue.Push(n)
}
func (q *Queue) Dequeue()(*Thing, bool){
v, ok := q.dequeue.Pop()
if ok{
return v, true
}
for {
v, ok := d.enqueue.Pop()
if !ok{
break
}
d.dequeue.Push(v)
}
return d.dequeue.Pop()
}
type Stack struct{
v []*Thing
}
func (s *Stack)Push(n *Thing){
s.v=append(s.v, n)
}
func (s *Stack) Pop()(*Thing, bool){
if len(s.v) == 0 {
return nil, false
}
lastIdx := len(s.v)-1
v := s.v[lastIdx]
s.v=s.v[:lastIdx]
return v, true
}
Upvotes: 0
Reputation: 4202
I implemented a queue that will expand the underlying buffer automatically:
package types
// Note: this queue does not shrink the underlying buffer.
type queue struct {
buf [][4]int // change to the element data type that you need
head int
tail int
}
func (q *queue) extend(need int) {
if need-(len(q.buf)-q.head) > 0 {
if need-len(q.buf) <= 0 {
copy(q.buf, q.buf[q.head:q.tail])
q.tail = q.tail - q.head
q.head = 0
return
}
newSize := len(q.buf) * 2
if newSize == 0 {
newSize = 100
}
newBuf := make([][4]int, newSize)
copy(newBuf, q.buf[q.head:q.tail])
q.buf = newBuf
q.tail = q.tail - q.head
q.head = 0
}
}
func (q *queue) push(p [4]int) {
q.extend(q.tail + 1)
q.buf[q.tail] = p
q.tail++
}
func (q *queue) pop() [4]int {
r := q.buf[q.head]
q.head++
return r
}
func (q *queue) size() int {
return q.tail - q.head
}
// put the following into queue_test.go
package types
import (
"testing"
"github.com/stretchr/testify/assert"
)
func TestQueue(t *testing.T) {
const total = 1000
q := &queue{}
for i := 0; i < total; i++ {
q.push([4]int{i, i, i, i})
assert.Equal(t, i+1, q.size())
}
for i := 0; i < total; i++ {
v := q.pop()
assert.Equal(t, [4]int{i, i, i, i}, v)
assert.Equal(t, total-1-i, q.size())
}
}
Upvotes: 1
Reputation: 1779
Unfortunately queues aren't currently part of the go standard library, so you need to write your own / import someone else's solution. It's a shame as containers written outside of the standard library aren't able to use generics.
A simple example of a fixed capacity queue would be:
type MyQueueElement struct {
blah int // whatever you want
}
const MAX_QUEUE_SIZE = 16
type Queue struct {
content [MAX_QUEUE_SIZE]MyQueueElement
readHead int
writeHead int
len int
}
func (q *Queue) Push(e MyQueueElement) bool {
if q.len >= MAX_QUEUE_SIZE {
return false
}
q.content[q.writeHead] = e
q.writeHead = (q.writeHead + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE
q.len++
return true
}
func (q *Queue) Pop() (MyQueueElement, bool) {
if q.len <= 0 {
return MyQueueElement{}, false
}
result := q.content[q.readHead]
q.content[q.readHead] = MyQueueElement{}
q.readHead = (q.readHead + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE
q.len--
return result, true
}
Gotchas avoided here include not having unbounded slice growth (caused by using the slice [1:] operation to discard), and zeroing out popped elements to ensure their contents are available for garbage collection. Note, in the case of a MyQueueElement struct containing only an int like here, it will make no difference, but if struct contained pointers it would.
The solution could be extended to reallocate and copy should an auto growing queue be desired.
This solution is not thread safe, but a lock could be added to Push/Pop if that is desired.
Playground https://play.golang.org/
Upvotes: 7

Reputation: 2141
In fact, if what you want is a basic and easy to use fifo queue, slice provides all you need.
queue := make([]int, 0)
// Push to the queue
queue = append(queue, 1)
// Top (just get next element, don't remove it)
x = queue[0]
// Discard top element
queue = queue[1:]
// Is empty ?
if len(queue) == 0 {
fmt.Println("Queue is empty !")
}
Of course, we suppose that we can trust the inner implementation of append and slicing so that it avoid useless resize and reallocation. For basic usage, this is perfectly sufficient.
Upvotes: 170
Reputation: 1586
I also implement the queue from slice as above. However, It's not thread-safe. So I decided to add a lock (mutex lock) to guarantee thread-safe.
package queue
import (
"sync"
)
type Queue struct {
lock *sync.Mutex
Values []int
}
func Init() Queue {
return Queue{&sync.Mutex{}, make([]int, 0)}
}
func (q *Queue) Enqueue(x int) {
for {
q.lock.Lock()
q.Values = append(q.Values, x)
q.lock.Unlock()
return
}
}
func (q *Queue) Dequeue() *int {
for {
if (len(q.Values) > 0) {
q.lock.Lock()
x := q.Values[0]
q.Values = q.Values[1:]
q.lock.Unlock()
return &x
}
return nil
}
return nil
}
You can check my solution on github here simple queue
Upvotes: 5

Reputation: 10677
Slice can be used to implement queue.
type queue struct {
values []*int
}
func New() *queue {
queue := &queue{}
return queue
}
func (q *queue) enqueue(val *int) {
q.values = append(q.values, val)
}
//deque function
Update:
here is complete implementation on my GitHub page https://github.com/raiskumar/algo-ds/blob/master/tree/queue.go
Upvotes: -2
Reputation: 79
Using a slice and an appropriate ("circular") indexing scheme on top still seems to be the way to go. Here's my take on it: https://github.com/phf/go-queue The benchmarks there also confirm that channels are faster, but at the price of more limited functionality.
Upvotes: 7

Reputation: 2877
Surprised to see no one has suggested buffered channels yet, for size bound FIFO Queue anyways.
//Or however many you might need + buffer.
c := make(chan int, 300)
//Push
c <- value
//Pop
x <- c
Upvotes: 127

Reputation: 1327804
To expand on the implementation side, Moraes proposes in his gist some struct from queue and stack:
// Stack is a basic LIFO stack that resizes as needed.
type Stack struct {
nodes []*Node
count int
}
// Queue is a basic FIFO queue based on a circular list that resizes as needed.
type Queue struct {
nodes []*Node
head int
tail int
count int
}
You can see it in action in this playground example.
Upvotes: 7
Reputation: 24557
Either vector or list should work, but vector is probably the way to go. I say this because vector will probably allocate less often than list and garbage collection (in the current Go implementation) is fairly expensive. In a small program it probably won't matter, though.
Upvotes: 12
Related Questions
- Best implementation of Java Queue?
- FIFO based Queue implementations?
- java Queue Interface
- Blocking FIFO Queue with Ability to Skip Elements?
- implement of a queue(fifo)
- Make my own FIFO Queue class for my own class object to fill it?
- Implementing a basic FIFO queue in Java
- Java FIFO queue implementation
- java fifo queue that allows pushing back?
- How to build a Terabyte queue?