Reputation: 49633
Looking for ways for a robot to locate itself in the house
I am hacking a vacuum cleaner robot to control it with a microcontroller (Arduino). I want to make it more efficient when cleaning a room. For now, it just go straight and turn when it hits something.
But I have trouble finding the best algorithm or method to use to know its position in the room. I am looking for an idea that stays cheap (less than $100) and not to complex (one that don't require a PhD thesis in computer vision). I can add some discrete markers in the room if necessary.
Right now, my robot has:
- One webcam
- Three proximity sensors (around 1 meter range)
- Compass (no used for now)
- Wi-Fi
- Its speed can vary if the battery is full or nearly empty
- A netbook Eee PC is embedded on the robot
Do you have any idea for doing this? Does any standard method exist for these kind of problems?
Note: if this question belongs on another website, please move it, I couldn't find a better place than Stack Overflow.
Upvotes: 51
Views: 19057
Answers (10)

Reputation: 3031
Use Ultra Sonic Sensor HC-SR04 or similar. As above told sense the walls distance from robot with sensors and room part with QR code.
When your are near to a wall turn 90 degree and move as width of your robot and again turn 90deg( i.e. 90 deg left turn) and again move your robot I think it will help :)
Upvotes: 1
Reputation: 429
You have a camera you said ? Did you consider looking at the ceiling ? There is little chance that two rooms have identical dimensions, so you can identify in which room you are, position in the room can be computed from angular distance to the borders of the ceiling and direction can probably be extracted by the position of doors.
This will require some image processing but the vacuum cleaner moving slowly to be efficiently cleaning will have enough time to compute.
Good luck !
Upvotes: 1
Reputation: 11
I was thinking about this problem too. But I don't understand why you can't just triangulate? Have two or three beacons (e.g. IR LEDs of different frequencies) and a IR rotating sensor 'eye' on a servo. You could then get an almost constant fix on your position. I expect the accuracy would be in low cm range and it would be cheap. You can then map anything you bump into easily.
Maybe you could also use any interruption in the beacon beams to plot objects that are quite far from the robot too.
Upvotes: 1
Reputation: 6733
Ever considered GPS? Every position on earth has a unique GPS coordinates - with resolution of 1 to 3 metres, and doing differential GPS you can go down to sub-10 cm range - more info here:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Global_Positioning_System
And Arduino does have lots of options of GPS-modules:
http://www.arduino.cc/playground/Tutorials/GPS
After you have collected all the key coordinates points of the house, you can then write the routine for the arduino to move the robot from point to point (as collected above) - assuming it will do all those obstacles avoidance stuff.
More information can be found here:
http://www.google.com/search?q=GPS+localization+robots&num=100
And inside the list I found this - specifically for your case: Arduino + GPS + localization:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u7evnfTAVyM
Upvotes: 1
Reputation: 5577
This doesn't replace the accepted answer (which is great, thanks!) but I might recommend getting a Kinect and use that instead of your webcam, either through Microsoft's recently released official drivers or using the hacked drivers if your EeePC doesn't have Windows 7 (presumably it does not).
That way the positioning will be improved by the 3D vision. Observing landmarks will now tell you how far away the landmark is, and not just where in the visual field that landmark is located.
Regardless, the accepted answer doesn't really address how to pick out landmarks in the visual field, and simply assumes that you can. While the Kinect drivers may already have feature detection included (I'm not sure) you can also use OpenCV for detecting features in the image.
Upvotes: 5
Reputation: 35944
The problem of figuring out a robot's position in its environment is called localization. Computer science researchers have been trying to solve this problem for many years, with limited success. One problem is that you need reasonably good sensory input to figure out where you are, and sensory input from webcams (i.e. computer vision) is far from a solved problem.
If that didn't scare you off: one of the approaches to localization that I find easiest to understand is particle filtering. The idea goes something like this:
- You keep track of a bunch of particles, each of which represents one possible location in the environment.
- Each particle also has an associated probability that tells you how confident you are that the particle really represents your true location in the environment.
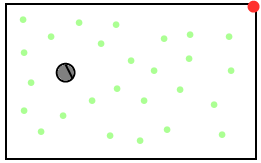
- When you start off, all of these particles might be distributed uniformly throughout your environment and be given equal probabilities. Here the robot is gray and the particles are green.
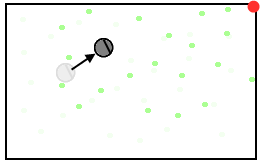
- When your robot moves, you move each particle. You might also degrade each particle's probability to represent the uncertainty in how the motors actually move the robot.
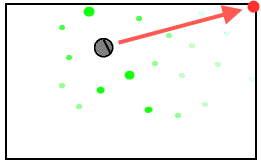
- When your robot observes something (e.g. a landmark seen with the webcam, a wifi signal, etc.) you can increase the probability of particles that agree with that observation.
- You might also want to periodically replace the lowest-probability particles with new particles based on observations.
- To decide where the robot actually is, you can either use the particle with the highest probability, the highest-probability cluster, the weighted average of all particles, etc.
If you search around a bit, you'll find plenty of examples: e.g. a video of a robot using particle filtering to determine its location in a small room.
Particle filtering is nice because it's pretty easy to understand. That makes implementing and tweaking it a little less difficult. There are other similar techniques (like Kalman filters) that are arguably more theoretically sound but can be harder to get your head around.
Upvotes: 38
Reputation: 1239

A QR Code poster in each room would not only make an interesting Modern art piece, but would be relatively easy to spot with the camera!
Upvotes: 8
Reputation: 5767
If you can place some markers in the room, using the camera could be an option. If 2 known markers have an angular displacement (left to right) then the camera and the markers lie on a circle whose radius is related to the measured angle between the markers. I don't recall the formula right off, but the arc segment (on that circle) between the markers will be twice the angle you see. If you have the markers at known height and the camera is at a fixed angle of inclination, you can compute the distance to the markers. Either of these methods alone can nail down your position given enough markers. Using both will help do it with fewer markers.
Unfortunately, those methods are imperfect due to measurement errors. You get around this by using a Kalman estimator to incorporate multiple noisy measurements to arrive at a good position estimate - you can then feed in some dead reckoning information (which is also imperfect) to refine it further. This part is goes pretty deep into math, but I'd say it's a requirement to do a great job at what you're attempting. You can do OK without it, but if you want an optimal solution (in terms of best position estimate for given input) there is no better way. If you actually want a career in autonomous robotics, this will play large in your future. (
Once you can determine your position you can cover the room in any pattern you'd like. Keep using the bump sensor to help construct a map of obstacles and then you'll need to devise a way to scan incorporating the obstacles.
Not sure if you've got the math background yet, but here is the book: http://books.google.com/books/about/Applied_optimal_estimation.html?id=KlFrn8lpPP0C
Upvotes: 6

Reputation: 1813
Assuming you are not looking for a generalised solution, you may actually know the room's shape, size, potential obstacle locations, etc. When the bot exists the factory there is no info about its future operating environment, which kind of forces it to be inefficient from the outset. If that's you case, you can hardcode that info, and then use basic measurements (ie. rotary encoders on wheels + compass) to precisely figure out its location in the room/house. No need for wifi triangulation or crazy sensor setups in my opinion. At least for a start.
Upvotes: 3
Reputation: 5259
One solution would be to use a strategy similar to "flood fill" (wikipedia). To get the controller to accurately perform sweeps, it needs a sense of distance. You can calibrate your bot using the proximity sensors: e.g. run motor for 1 sec = xx change in proximity. With that info, you can move your bot for an exact distance, and continue sweeping the room using flood fill.
Upvotes: 3
Related Questions
- Autonomous robot location detection indoors
- Algorithm to calculate route for indoor positioning system
- Line follower bot location
- Using the GPS to detect whether an android device is indoors
- Indoor positioning system in android
- Suggestion on Robotic Localization
- Indoor positioning of a moving object in 3D space
- Android: How to identify programmatically if device is located indoors?
- How to track position of an Android device in a building?
- Monte Carlo Localization example